Summary
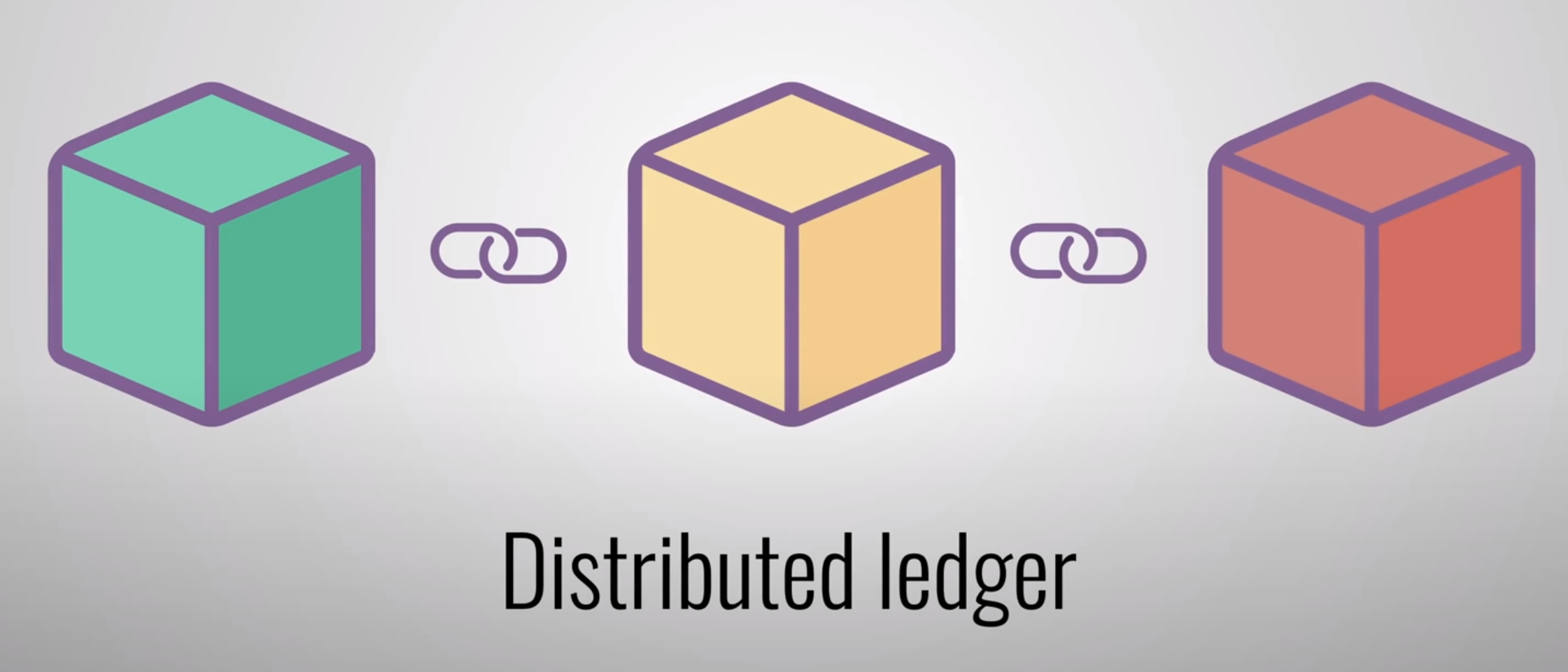
- A blockchain is a distributed database that is shared among the nodes of a computer network.
- As a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in digital format.
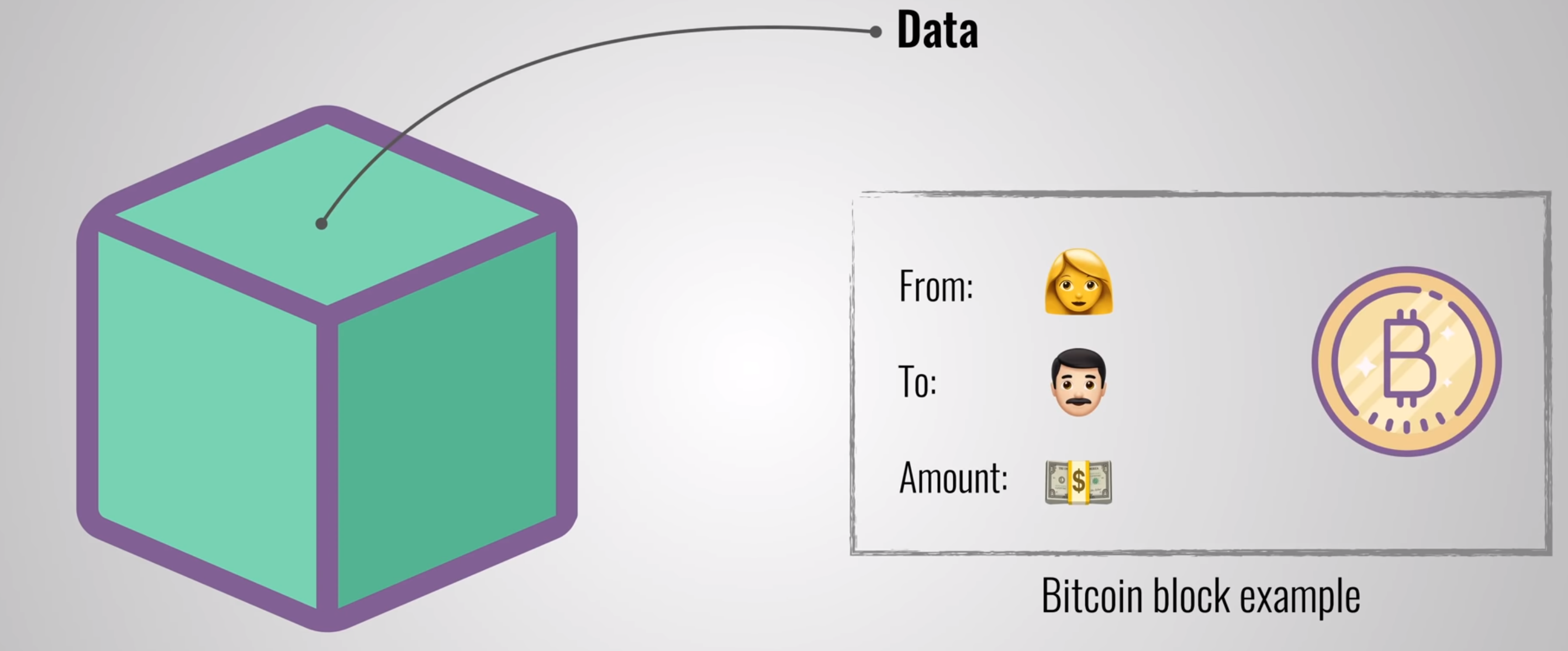
- Blockchains are best known for their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems, such as Bitcoin, for maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions.
- The innovation with a blockchain is that it guarantees the fidelity and security of a record of data and generates trust without the need for a trusted third party.
Another definition
Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding). Virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network, reducing risk and cutting costs for all involved. ref
How it works?
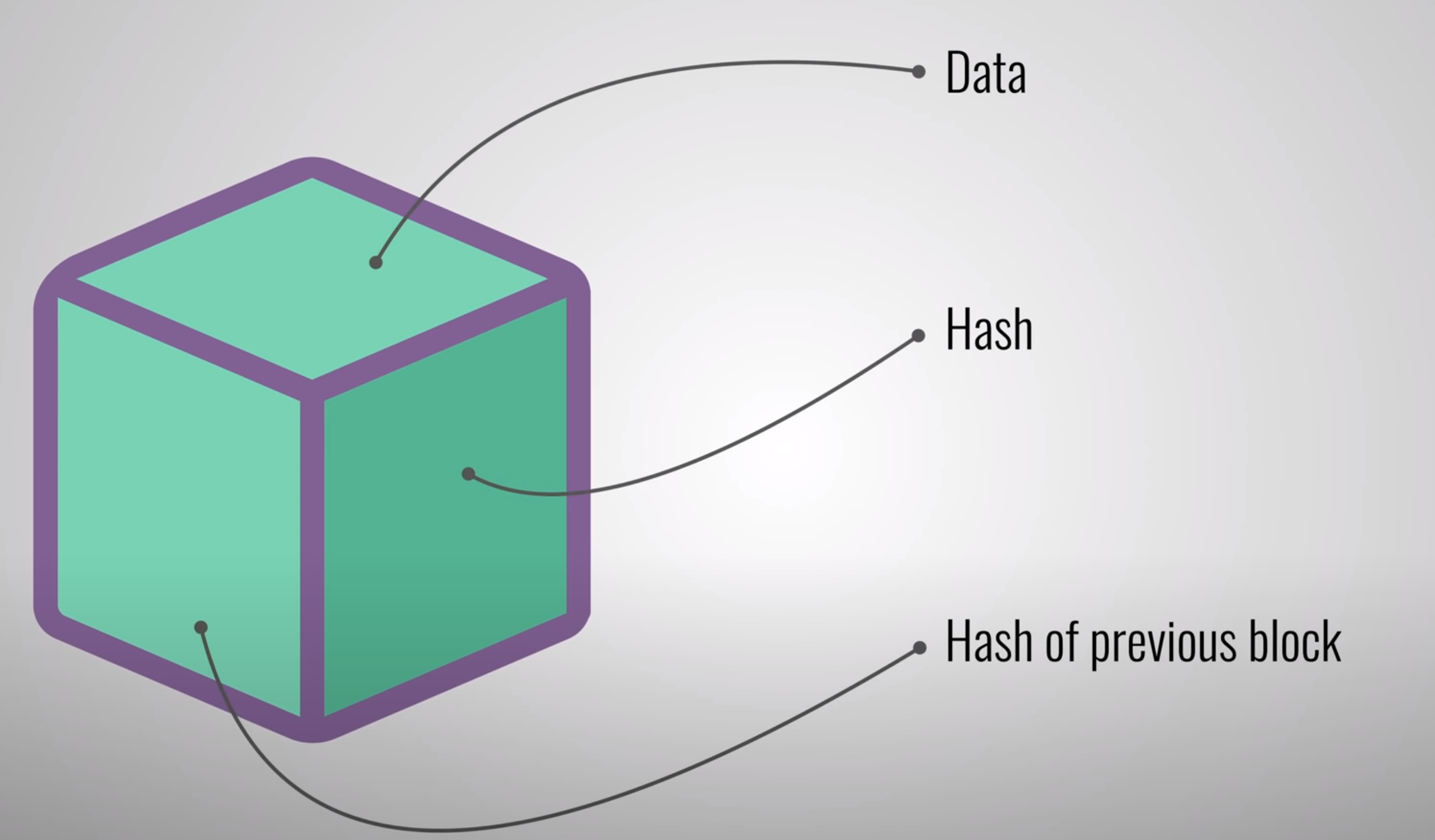
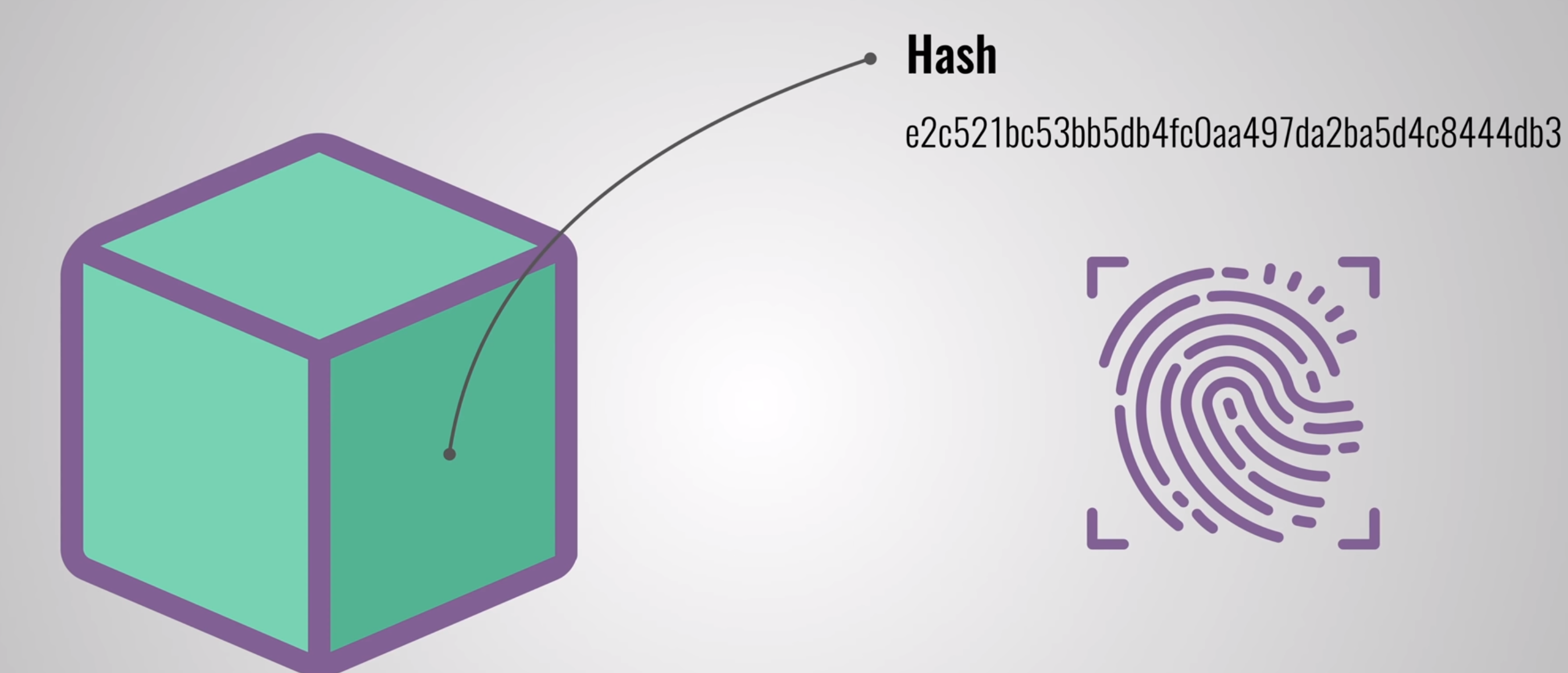
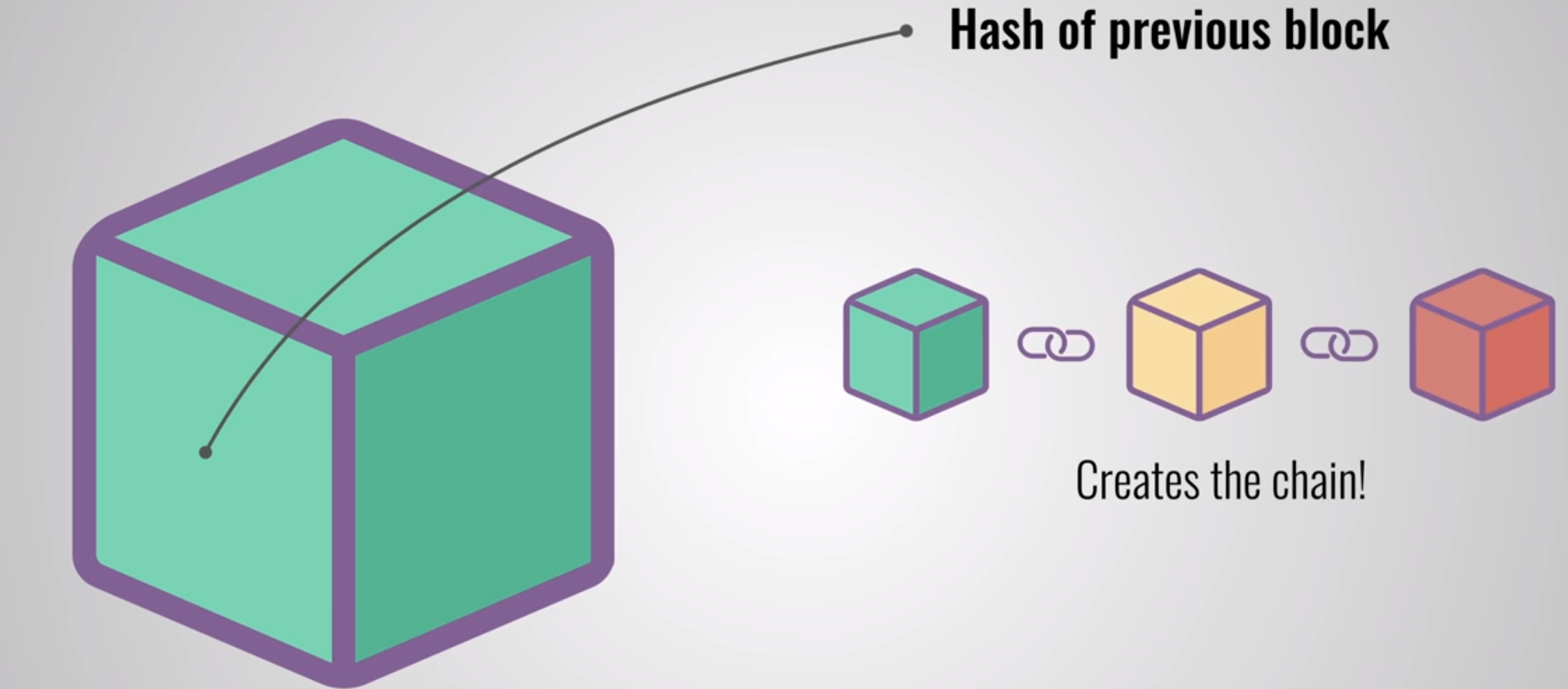
blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked together using cryptography.
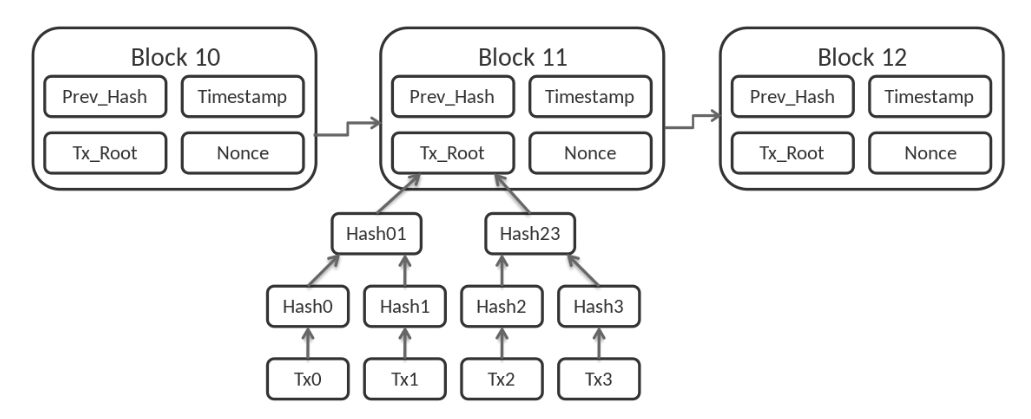
 Proof of work
Proof of work
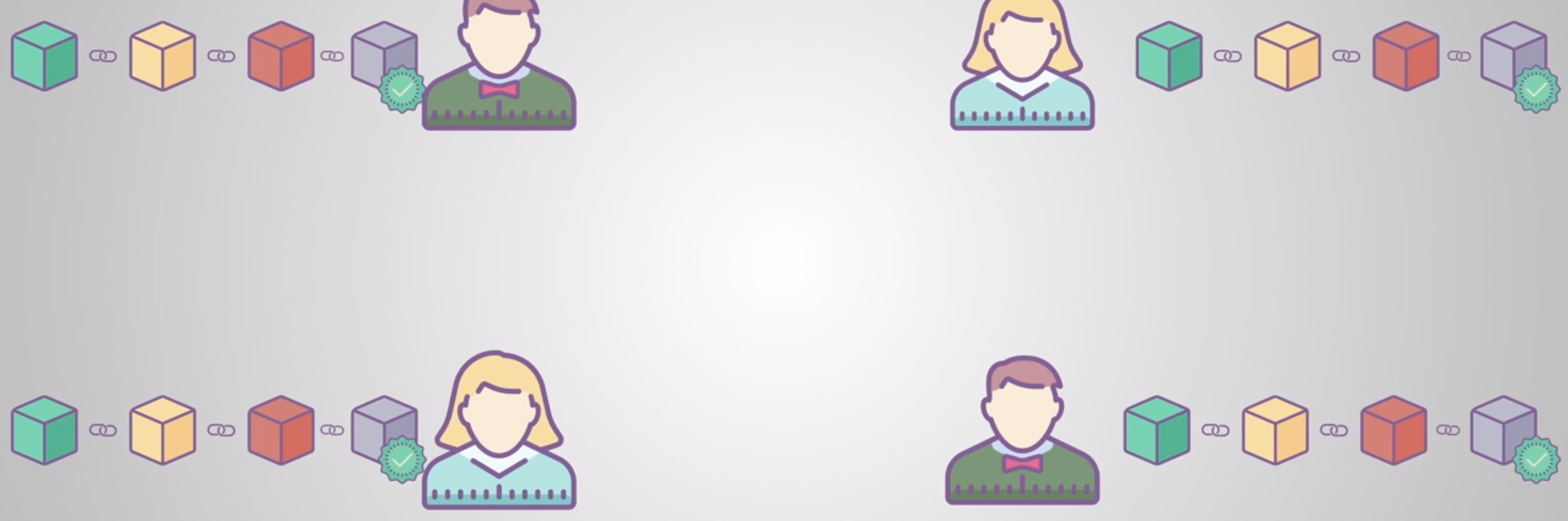
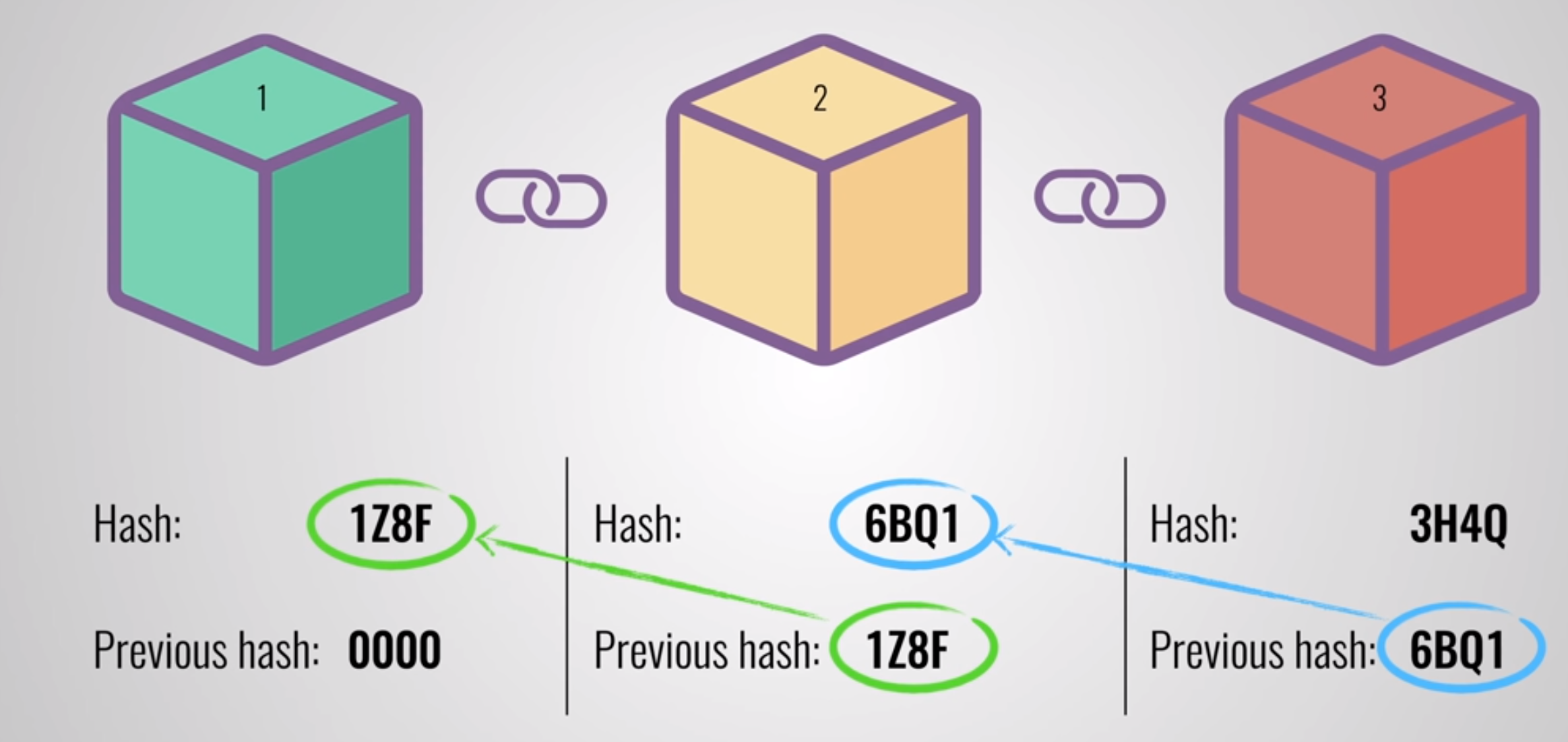
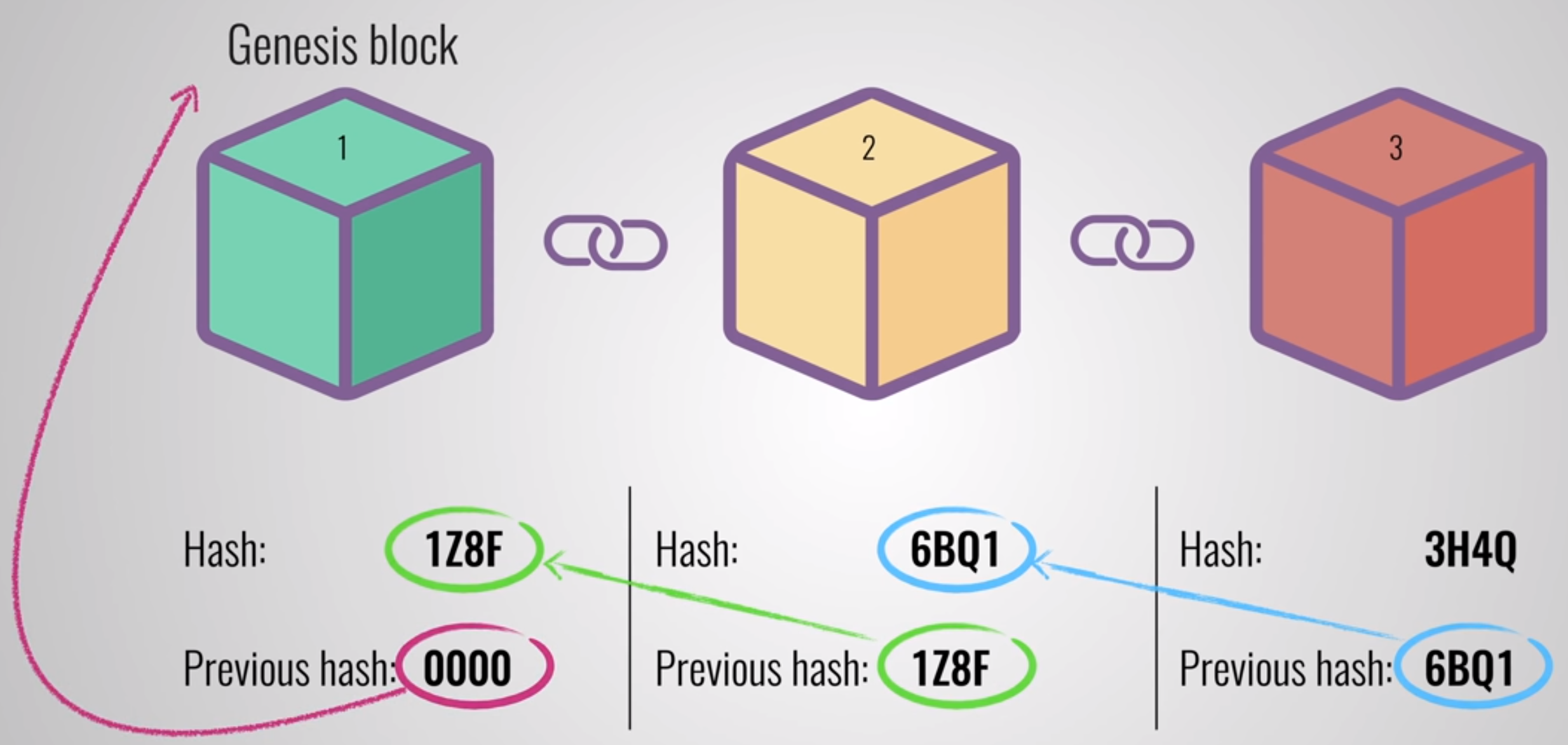
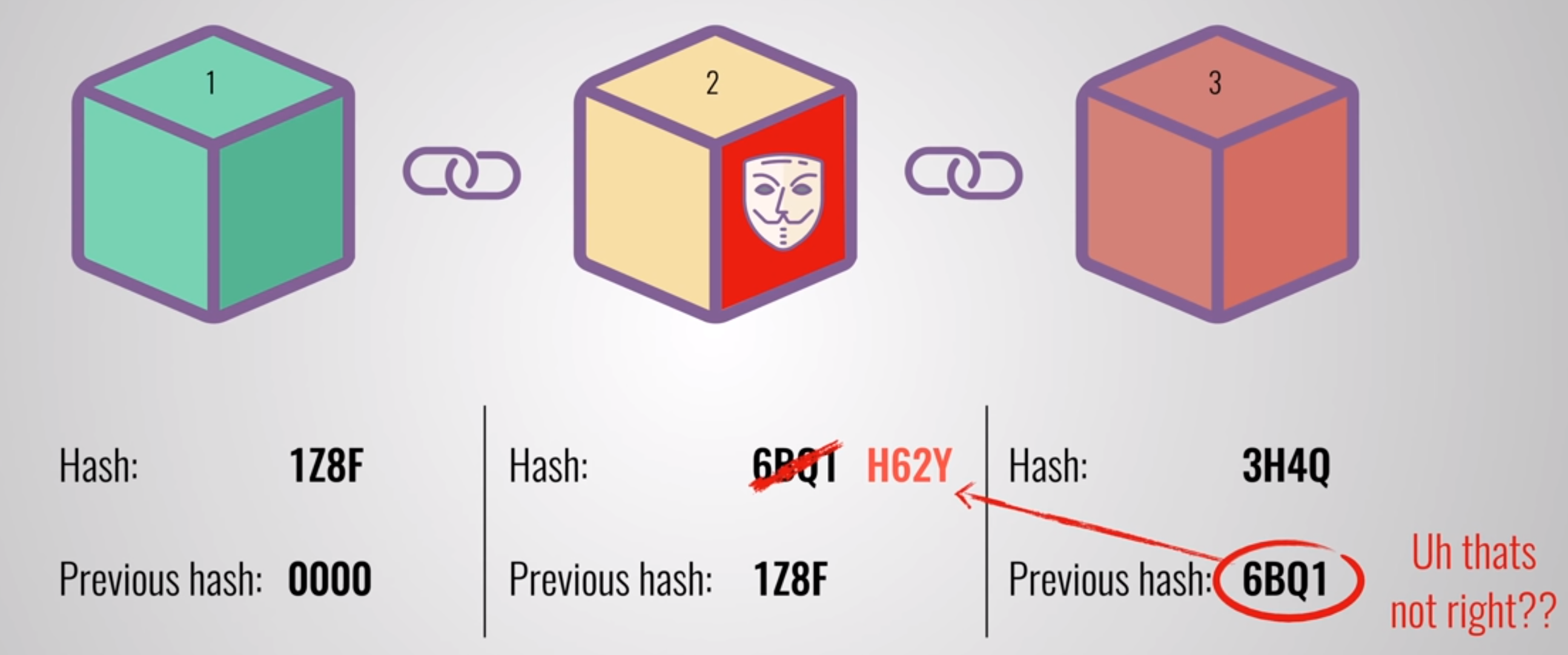

 To tamper a block the hacker should have to change all the blocks in the chain, redo the proof of
work for each block and take control of more than 50% of the peer to peer network to update the
record in all the nodes of the network. This is almost impossible to do.
To tamper a block the hacker should have to change all the blocks in the chain, redo the proof of
work for each block and take control of more than 50% of the peer to peer network to update the
record in all the nodes of the network. This is almost impossible to do.

Proof of work
- Generating just any hash for a set of bitcoin transactions would be trivial for a modern computer, so in order to turn the process into “work," the bitcoin network sets a certain level of
“difficulty.”
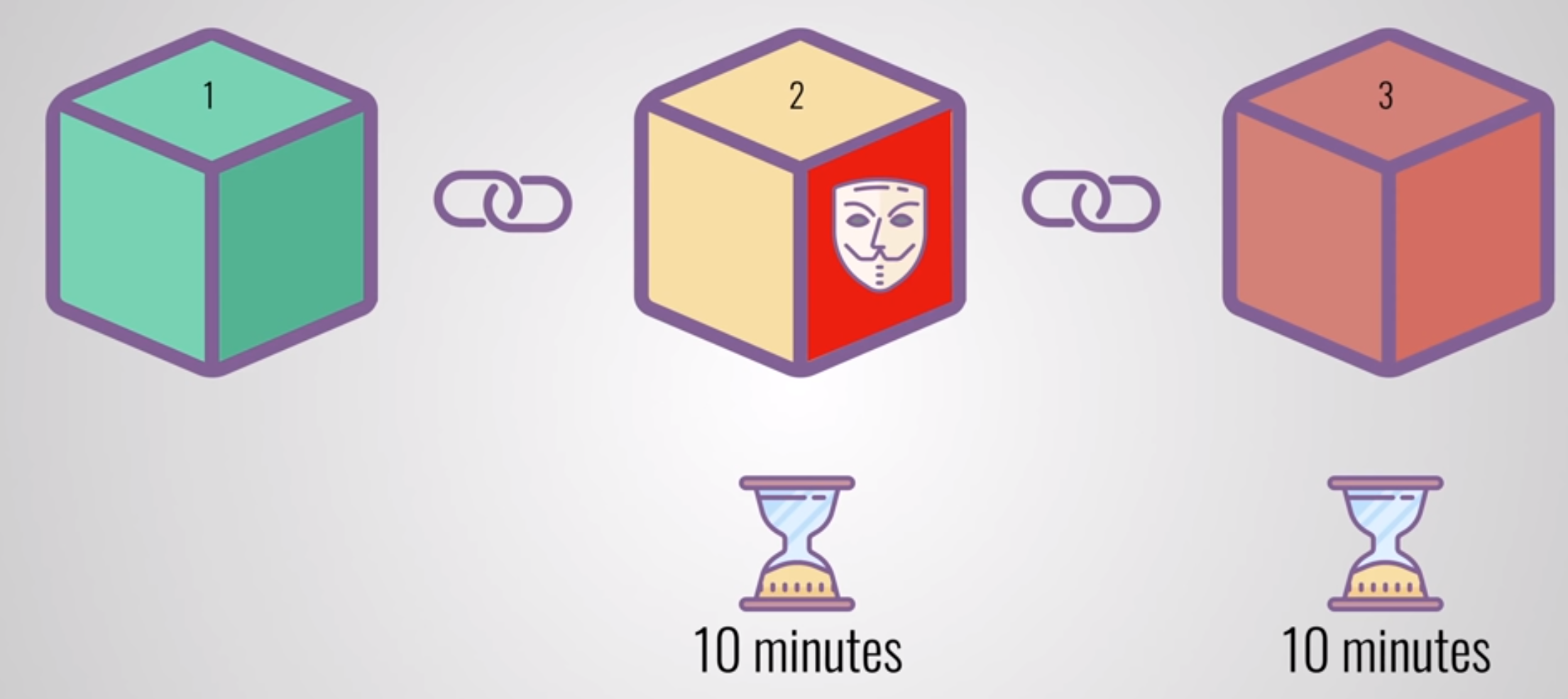
- This setting is adjusted so that a new block is “mined” – added to the blockchain by generating a valid hash – approximately every 10 minutes.
- Setting difficulty is accomplished by establishing a “target” for the hash: the lower the target, the smaller the set of valid hashes, and the harder it is to generate one. *In practice, this means a hash that starts with a very long string of zeros.