related:
django-cors-headers : the middleware configured will add CORS headers to the response and CORS_ORIGIN_WHITELIST decide what origins can access resources
Details fc
| position | ease | box | interval | due |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| front | 2.5 | 0 | 0 | 2021-09-12T07:59:52Z |
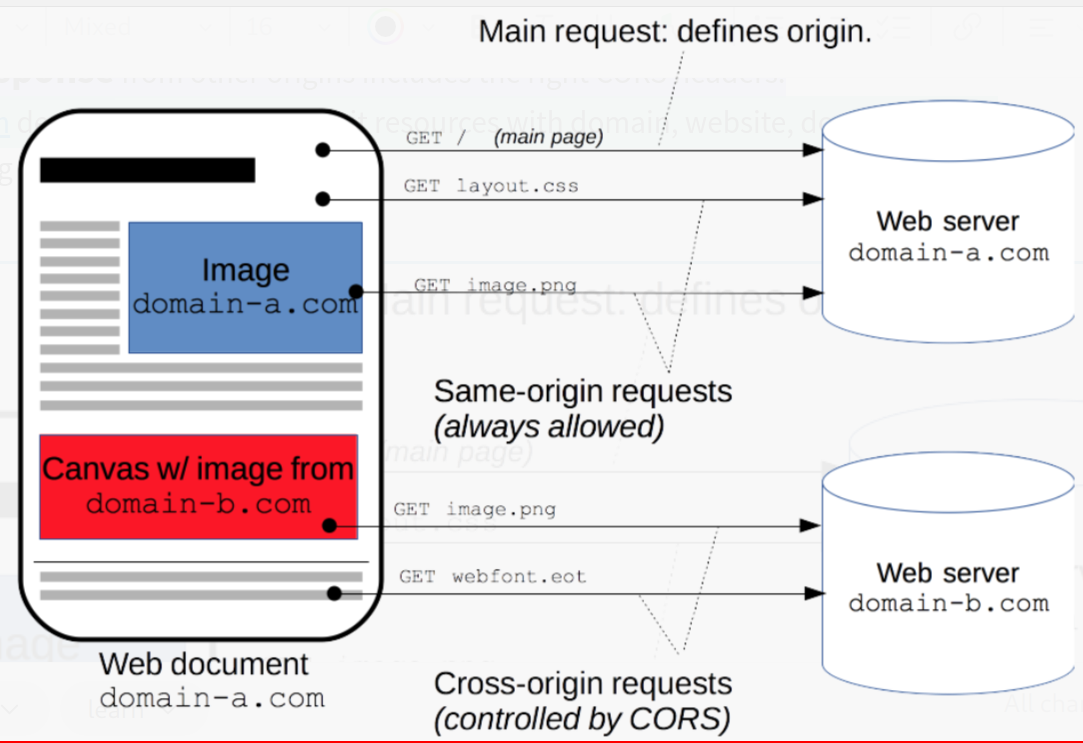
- Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a mechanism that uses additional HTTP headers to tell browsers to give a web application running at one origin, access to selected resources from a different origin.
- A web application executes a cross-origin HTTP request when it requests a resource that has a different origin (domain, protocol, or port) from its own.
An example of a cross-origin request: the front-end JavaScript code served from https://domain-a.com uses XMLHttpRequest to make a request for https://domain-b.com/data.json.
- For security reasons, browsers restrict cross-origin HTTP requests initiated from scripts.
- For example, XMLHttpRequest and the Fetch API follow the Same-Origin Policy.
- This means that a web application using those APIs can only request resources from the same origin the application was loaded from,
- unless the response from other origins includes the right CORS headers.
- domain-b.com decides whether to share it resources with domain, website, domain-a.com.
- by sharing CORS headers in response